Digital Tomography in Dentistry
What is Digital Tomography? What are the Benefits?
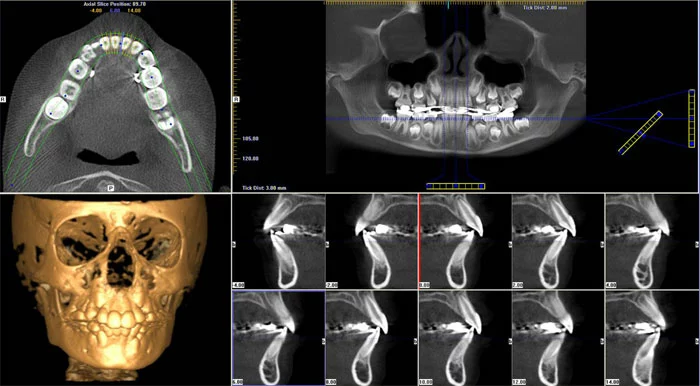
Imaging methods are very important in terms of diagnosis and treatment in dentistry. From the discovery of X-rays to this day, with the advancement of technology, significant progress has been made in obtaining images. After the use of digital tomography in dentistry in addition to traditional methods, images (3D) were obtained with 3D digital tomography. With computer software, different sections were obtained from these images and the objects were examined spatially from all directions.
Digital tomographs obtain detailed and clear images by taking sections at shorter intervals, and these sections are combined and colored in the computer environment to obtain 3D images. Due to the wide range of possibilities, it offers, it finds a wide range of uses in endodontic treatment, orthodontics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, pedodontics, and prosthetic and implant applications.
Compared to the old tomography system, more successful and clearer images are obtained and it allows to make clearer decisions for treatment. In addition, since it is colored in the computer environment and displayed in 3D, convenience is provided in the treatment steps.
Advantages of Digital Tomography
- In cases where 2D films such as periapical, occlusal and panoramic films are insufficient, 3D digital tomography provides great convenience in implant planning, imaging of intrachain cyst and tumor-like pathologies.
- With digital tomography, the radiation dose is reduced compared to conventional (conventional) tomography.
- Measurements can be made easily on images obtained by digital tomography. Thus, the diameter and length of the implant to be applied in implant surgery can be planned before the implant surgery on the image taken by digital tomography.
- In images taken with digital tomography, bone density can be known with numerical precision.
Uses of Digital Tomography
- Planning before operations in the maxillofacial region,
- Surgical template making before implant placement,
- Examination of anatomical structures such as nasal cavity, sinus cavity, mandibular nerve,
- Examination of bone quality and density,
- Examination of the jaw joint,
- Determination of the positions of impacted teeth,
- Examination of cysts and tumor-like structures,
- Examination of root fractures,
- It is used in bone graft application.